Search This Blog
Tuesday, September 27, 2011
Sunday, September 25, 2011
Composites and Advanced Materials
For many years, aircraft designers could propose theoretical designs that they could not build because the materials needed to construct them did not exist. (The term "unobtainium" is sometimes used to identify materials that are desired but not yet available.) For instance, large spaceplanes like the Space Shuttle would have proven extremely difficult, if not impossible, to build without heat-resistant ceramic tiles to protect them during reentry. And high-speed forward-swept-wing airplanes like Grumman's experimental X-29 or the Russian Sukhoi S-27 Berkut would not have been possible without the development of composite materials to keep their wings from bending out of shape.
Composites are the most important materials to be adapted for aviation since the use of aluminum in the 1920s. Composites are materials that are combinations of two or more organic or inorganic components. One material serves as a "matrix," which is the material that holds everything together, while the other material serves as a reinforcement, in the form of fibers embedded in the matrix. Until recently, the most common matrix materials were "thermosetting" materials such as epoxy, bismaleimide, or polyimide. The reinforcing materials can be glass fiber, boron fiber, carbon fiber, or other more exotic mixtures.
Fiberglass is the most common composite material, and consists of glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix. Fiberglass was first used widely in the 1950s for boats and automobiles, and today most cars have fiberglass bumpers covering a steel frame. Fiberglass was first used in the Boeing 707 passenger jet in the 1950s, where it comprised about two percent of the structure. By the 1960s, other composite materials became available, in particular boron fiber and graphite, embedded in epoxy resins. The U.S. Air Force and U.S. Navy began research into using these materials for aircraft control surfaces like ailerons and rudders. The first major military production use of boron fiber was for the horizontal stabilizers on the Navy's F-14 Tomcat interceptor. By 1981, the British Aerospace-McDonnell Douglas AV-8B Harrier flew with over 25 percent of its structure made of composite materials.
Making composite structures is more complex than manufacturing most metal structures. To make a composite structure, the composite material, in tape or fabric form, is laid out and put in a mold under heat and pressure. The resin matrix material flows and when the heat is removed, it solidifies. It can be formed into various shapes. In some cases, the fibers are wound tightly to increase strength. One useful feature of composites is that they can be layered, with the fibers in each layer running in a different direction. This allows materials engineers to design structures that behave in certain ways. For instance, they can design a structure that will bend in one direction, but not another. The designers of the Grumman X-29 experimental plane used this attribute of composite materials to design forward-swept wings that did not bend up at the tips like metal wings of the same shape would have bent in flight.
The greatest value of composite materials is that they can be both lightweight and strong. The heavier an aircraft weighs, the more fuel it burns, so reducing weight is important to aeronautical engineers.
Despite their strength and low weight, composites have not been a miracle solution for aircraft structures. Composites are hard to inspect for flaws. Some of them absorb moisture. Most importantly, they can be expensive, primarily because they are labor intensive and often require complex and expensive fabrication machines. Aluminum, by contrast, is easy to manufacture and repair. Anyone who has ever gotten into a minor car accident has learned that dented metal can be hammered back into shape, but a crunched fiberglass bumper has to be completely replaced. The same is true for many composite materials used in aviation.
Modern airliners use significant amounts of composites to achieve lighter weight. About ten percent of the structural weight of the Boeing 777, for instance, is composite material. Modern military aircraft, such as the F-22, use composites for at least a third of their structures, and some experts have predicted that future military aircraft will be more than two-thirds composite materials. But for now, military aircraft use substantially greater percentages of composite materials than commercial passenger aircraft primarily because of the different ways that commercial and military aircraft are maintained.
Aluminum is a very tolerant material and can take a great deal of punishment before it fails. It can be dented or punctured and still hold together. Composites are not like this. If they are damaged, they require immediate repair, which is difficult and expensive. An airplane made entirely from aluminum can be repaired almost anywhere. This is not the case for composite materials, particularly as they use different and more exotic materials. Because of this, composites will probably always be used more in military aircraft, which are constantly being maintained, than in commercial aircraft, which have to require less maintenance.
Thermoplastics are a relatively new material that is replacing thermosets as the matrix material for composites. They hold much promise for aviation applications. One of their big advantages is that they are easy to produce. They are also more durable and tougher than thermosets, particularly for light impacts, such as when a wrench dropped on a wing accidentally. The wrench could easily crack a thermoset material but would bounce off a thermoplastic composite material.
In addition to composites, other advanced materials are under development for aviation. During the 1980s, many aircraft designers became enthusiastic about ceramics, which seemed particularly promising for lightweight jet engines, because they could tolerate hotter temperatures than conventional metals. But their brittleness and difficulty to manufacture were major drawbacks, and research on ceramics for many aviation applications decreased by the 1990s.
Aluminum still remains a remarkably useful material for aircraft structures and metallurgists have worked hard to develop better aluminum alloys (a mixture of aluminum and other materials). In particular, aluminum-lithium is the most successful of these alloys. It is approximately ten percent lighter than standard aluminum. Beginning in the later 1990s it was used for the Space Shuttle's large External Tank in order to reduce weight and enable the shuttle to carry more payload. Its adoption by commercial aircraft manufacturers has been slower, however, due to the expense of lithium and the greater difficulty of using aluminum-lithium (in particular, it requires much care during welding). But it is likely that aluminum-lithium will eventually become a widely used material for both commercial and military aircraft.
--Dwayne A. Day
Sources and further reading:
Christensen, R.M. Mechanics of Composite Materials. New York, John Wiley & Sons, 1979.
"Fiber Composite Materials." Papers Presented at a Seminar of the American Society for Metals, October 17 and 18, 1964, Metals Park, Ohio: American Society for Metals, 1965.
Hancox, N.L. Fibre Composite Hybrid Materials, New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., 1981.
Hoskin, B.C., and Baker, A.A., eds. Composite Materials for Aircraft Structures, New York: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Inc., 1984.
Kroschwitz, Jacqueline. High Performance Polymers and Composites, New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1991.
Noton, Bryan R. Engineering Applications of Composites. New York, Academic Press, 1974.
Tien, John K., and Caulfield, Thomas, eds. Superalloys, Supercomposites and Superceramics. New York: Academic Press, 1989.
Tsai, Stephen W. Introduction to Composite Materials, Westport, Conn.: Technomic Publishing Company, 1980.
Weeton, John W., Peters, Dean M., and Thomas, Karyn L., eds. Engineers' Guide to Composite Materials, Metals Park, Ohio: American Society for Metals, 1987.
Composites are the most important materials to be adapted for aviation since the use of aluminum in the 1920s. Composites are materials that are combinations of two or more organic or inorganic components. One material serves as a "matrix," which is the material that holds everything together, while the other material serves as a reinforcement, in the form of fibers embedded in the matrix. Until recently, the most common matrix materials were "thermosetting" materials such as epoxy, bismaleimide, or polyimide. The reinforcing materials can be glass fiber, boron fiber, carbon fiber, or other more exotic mixtures.
Fiberglass is the most common composite material, and consists of glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix. Fiberglass was first used widely in the 1950s for boats and automobiles, and today most cars have fiberglass bumpers covering a steel frame. Fiberglass was first used in the Boeing 707 passenger jet in the 1950s, where it comprised about two percent of the structure. By the 1960s, other composite materials became available, in particular boron fiber and graphite, embedded in epoxy resins. The U.S. Air Force and U.S. Navy began research into using these materials for aircraft control surfaces like ailerons and rudders. The first major military production use of boron fiber was for the horizontal stabilizers on the Navy's F-14 Tomcat interceptor. By 1981, the British Aerospace-McDonnell Douglas AV-8B Harrier flew with over 25 percent of its structure made of composite materials.
Making composite structures is more complex than manufacturing most metal structures. To make a composite structure, the composite material, in tape or fabric form, is laid out and put in a mold under heat and pressure. The resin matrix material flows and when the heat is removed, it solidifies. It can be formed into various shapes. In some cases, the fibers are wound tightly to increase strength. One useful feature of composites is that they can be layered, with the fibers in each layer running in a different direction. This allows materials engineers to design structures that behave in certain ways. For instance, they can design a structure that will bend in one direction, but not another. The designers of the Grumman X-29 experimental plane used this attribute of composite materials to design forward-swept wings that did not bend up at the tips like metal wings of the same shape would have bent in flight.
The greatest value of composite materials is that they can be both lightweight and strong. The heavier an aircraft weighs, the more fuel it burns, so reducing weight is important to aeronautical engineers.
Despite their strength and low weight, composites have not been a miracle solution for aircraft structures. Composites are hard to inspect for flaws. Some of them absorb moisture. Most importantly, they can be expensive, primarily because they are labor intensive and often require complex and expensive fabrication machines. Aluminum, by contrast, is easy to manufacture and repair. Anyone who has ever gotten into a minor car accident has learned that dented metal can be hammered back into shape, but a crunched fiberglass bumper has to be completely replaced. The same is true for many composite materials used in aviation.
Modern airliners use significant amounts of composites to achieve lighter weight. About ten percent of the structural weight of the Boeing 777, for instance, is composite material. Modern military aircraft, such as the F-22, use composites for at least a third of their structures, and some experts have predicted that future military aircraft will be more than two-thirds composite materials. But for now, military aircraft use substantially greater percentages of composite materials than commercial passenger aircraft primarily because of the different ways that commercial and military aircraft are maintained.
Aluminum is a very tolerant material and can take a great deal of punishment before it fails. It can be dented or punctured and still hold together. Composites are not like this. If they are damaged, they require immediate repair, which is difficult and expensive. An airplane made entirely from aluminum can be repaired almost anywhere. This is not the case for composite materials, particularly as they use different and more exotic materials. Because of this, composites will probably always be used more in military aircraft, which are constantly being maintained, than in commercial aircraft, which have to require less maintenance.
Thermoplastics are a relatively new material that is replacing thermosets as the matrix material for composites. They hold much promise for aviation applications. One of their big advantages is that they are easy to produce. They are also more durable and tougher than thermosets, particularly for light impacts, such as when a wrench dropped on a wing accidentally. The wrench could easily crack a thermoset material but would bounce off a thermoplastic composite material.
In addition to composites, other advanced materials are under development for aviation. During the 1980s, many aircraft designers became enthusiastic about ceramics, which seemed particularly promising for lightweight jet engines, because they could tolerate hotter temperatures than conventional metals. But their brittleness and difficulty to manufacture were major drawbacks, and research on ceramics for many aviation applications decreased by the 1990s.
Aluminum still remains a remarkably useful material for aircraft structures and metallurgists have worked hard to develop better aluminum alloys (a mixture of aluminum and other materials). In particular, aluminum-lithium is the most successful of these alloys. It is approximately ten percent lighter than standard aluminum. Beginning in the later 1990s it was used for the Space Shuttle's large External Tank in order to reduce weight and enable the shuttle to carry more payload. Its adoption by commercial aircraft manufacturers has been slower, however, due to the expense of lithium and the greater difficulty of using aluminum-lithium (in particular, it requires much care during welding). But it is likely that aluminum-lithium will eventually become a widely used material for both commercial and military aircraft.
--Dwayne A. Day
Sources and further reading:
Christensen, R.M. Mechanics of Composite Materials. New York, John Wiley & Sons, 1979.
"Fiber Composite Materials." Papers Presented at a Seminar of the American Society for Metals, October 17 and 18, 1964, Metals Park, Ohio: American Society for Metals, 1965.
Hancox, N.L. Fibre Composite Hybrid Materials, New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., 1981.
Hoskin, B.C., and Baker, A.A., eds. Composite Materials for Aircraft Structures, New York: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Inc., 1984.
Kroschwitz, Jacqueline. High Performance Polymers and Composites, New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1991.
Noton, Bryan R. Engineering Applications of Composites. New York, Academic Press, 1974.
Tien, John K., and Caulfield, Thomas, eds. Superalloys, Supercomposites and Superceramics. New York: Academic Press, 1989.
Tsai, Stephen W. Introduction to Composite Materials, Westport, Conn.: Technomic Publishing Company, 1980.
Weeton, John W., Peters, Dean M., and Thomas, Karyn L., eds. Engineers' Guide to Composite Materials, Metals Park, Ohio: American Society for Metals, 1987.
Anti-oxidation coatings (EVU-5)
EVU-5 anti-oxidation coatings are intended for oxidation protection and operability assurance of carbon-carbon and carbon-ceramic composite materials at temperatures up to 2000°C.
Main characteristics
Service temperature, °C
до 2000
Thickness, μm
100-150
Emittance (coefficient), relative units
More than 0,8
Linear Thermal Expansion Coefficient, 1/°С
4.8-5.2´10-6
Items of carbon-carbon and carbon-ceramic composites with anti-oxidation coating at working temperature of 2000°C
Erosion-resistant coating on heat-insulating material
Main characteristics
Service temperature, °C
до 2000
Thickness, μm
100-150
Emittance (coefficient), relative units
More than 0,8
Linear Thermal Expansion Coefficient, 1/°С
4.8-5.2´10-6
Items of carbon-carbon and carbon-ceramic composites with anti-oxidation coating at working temperature of 2000°C
Erosion-resistant coating on heat-insulating material
c++ and Computer Graphic Design
these project's was in my first course of aerospace eng
Write a C++ program employing the case operator. Input data should be typed in from the keyboard. Calculate the total area of geometric figure.
Write a C++ program employing the case operator. Input data should be typed in from the keyboard. Calculate the total area of geometric figure.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main (string[] args)
{
double s=0, r=0 ,h=0;
int k = 0;
Console.Write("\n Area Menu " );
Console.Write("\n 0. Area of circle " );
Console.Write("\n 1. Area of spher " );
Console.Write("\n 2. Area of cylinder " );
Console.Write("\n 3. Area of triangle " );
Console.Write("\n a number(less than 3) : " );
k = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
switch (k)
{
case 0:
Console.Write("\n enter the radius ");
r = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
s = Math.PI * r * r;
break;
case 1:
Console.Write("\n enter the radius ");
r = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
s = Math.PI * r * r;
break;
case 2:
Console.Write("\n enter the radius and height ");
r = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
h = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
s = 2 * Math.PI * r * h;
break;
case 3:
Console.Write("\n enter the radius and height ");
r = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
h = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
s = (r * h) / 2;
break;
default :
Console.Write("\n input invalid ");
break;
}
Console.Write("\n the area is {0} ", s);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
task 8
Task 2. Define variables x and a. Calculate the value of the expression Y with using if operator. Check all abnormal situations in which function does not exist.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace mehdi_task_8_2
{
class Program
{
static void input(ref double a, ref double x)
{
Console.WriteLine(" Enter a value for x : ");
x = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine(" Enter a value for a : ");
a = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
}
static double process(double a , double x)
{
Double Y;
if (x <= (-6 * a))
Y = -Math.Pow(x + 3 * a, 2) - 2 * a;
else
Y = a * Math.Cos(x + 3 * a) - 3 * a;
return Y;
}
static void output (double Y)
{
Console.Write(" The Value of Y is {0}", Y ) ;
Console.ReadLine( ) ;
}
static void Main (string[] args)
{
Double x=0 , a=0 , Y=0;
input ( ref a , ref x );
Y = process (a,x) ;
output(Y) ;
}
}
}
task8
Task 1. Write a program that asks a user to enter coordinates and define whether this coordinate belong to the shaded area.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace mehdi_task_8_1
{
class Program
{
static void input(ref double x, ref double y)
{
Console.WriteLine(" Enter a value for x : ");
x = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine(" Enter a value for y : ");
y = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
}
static int process(double x, double y)
{
int answer;
if ((x <= 2) & (x >= -2) & (y >= -2) & (y <= 2) & ((x + y - 1 > 0) | (-x + y + 1 < 0) | (-x - y - 1 > 0) | (x - y + 1 < 0)))
answer = 1;
else
answer = 2;
return answer;
}
static void output(int ans1)
{
switch (ans1)
{
case 1:
Console.WriteLine("\n The given Co-ordinate is inside the shaded area");
break;
case 2:
Console.WriteLine("\n The given Co-ordinate is outside the shaded area");
break;
}
}
static void Main (string[] args)
{
double x = 0, y = 0;
int ans = 0;
input(ref x, ref y);
ans = process(x, y);
output(ans);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
------------------------------------------------------------ task 7
DO the following as a single program using files & functions :
1.calculate value of the next expression:
3- Print out author’s full name, if first name –mehdi , and surname – moghadasi.
4- Write a program that asks a user to enter coordinates and define whether
this coordinate belong to the shaded area.
5-Define variables x and a. Calculate the value of the expression Y with using if operator. Check all abnormal situations in which function does not exist.
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void input()
{
double x, y, x1, a;
Console.Write("\n Enter The X - Co-ordinate : ");
x = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("\n Enter The Y - Co-ordinate : ");
y = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("\n Enter A Value For x : ");
x1 = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("\n Enter A Value For a : ");
a = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
StreamWriter sr2 = new StreamWriter("file2.txt");
sr2.Write(x + " ");
sr2.Write(y + " ");
sr2.Write(x1 + " ");
sr2.Write(a + " ");
sr2.Close();
}
static void condition()
{
string strline1, strline2;
string[] strarr1;
string[] strarr2;
double denom = 0, num = 0, y1 = 0, Y = 0;
bool Z1 = true;
int ans = 0;
StreamReader sr1 = new StreamReader("file.txt");
strline1 = sr1.ReadLine();
strarr1 = strline1.Split(' ');
double X = double.Parse(strarr1[0]);
double a1 = double.Parse(strarr1[1]);
double X1 = double.Parse(strarr1[3]);
double Y1 = double.Parse(strarr1[4]);
bool A1 = bool.Parse(strarr1[5]);
bool B1 = bool.Parse(strarr1[6]);
bool C1 = bool.Parse(strarr1[7]);
double beta = double.Parse(strarr1[2]);
sr1.Close();
StreamReader sr3 = new StreamReader("file2.txt");
strline2 = sr3.ReadLine();
strarr2 = strline2.Split(' ');
double x = double.Parse(strarr2[0]);
double y = double.Parse(strarr2[1]);
double x2 = double.Parse(strarr2[2]);
double a = double.Parse(strarr2[3]);
sr3.Close();
num = Math.Sin(Math.PI - beta / 2) + Math.Log10(2 * X + Math.Pow(a1, 2)) + Math.Pow(X, 2) + Math.Pow(Math.Abs(X - Math.Pow(a1, 3)), 0.25);
denom = Math.Exp(X + a1) + Math.Pow(X, 3) + 5.4 * Math.Pow(10, -4) + Math.Tan(Math.Pow(X, 2) + 0.5 * Math.Pow(10, 2.1));
y1 = num / denom;
Z1 = A1 || B1 && X1 < Y1 || (X1 < 1.5 || B1 && C1);
if ((x <= 2) & (x >= -2) & (y >= -2) & (y <= 2) & ((x + y - 1 > 0) | (-x + y + 1 < 0) | (-x - y - 1 > 0) | (x - y + 1 < 0)))
ans = 1;
else
ans = 2;
if (x2 <= (-6 * a))
Y = -Math.Pow(x + 3 * a, 2) - 2 * a;
else
Y = a * Math.Cos(x + 3 * a) - 3 * a;
StreamWriter sr2 = new StreamWriter("file1.txt");
sr2.Write(Z1 + " ");
sr2.Write(ans + " ");
sr2.Write(Y + " ");
sr2.Close();
}
static void output()
{
string strline, strline2, strline3, fullname;
string[] strarr;
string[] strarr2;
string[] strarr3;
StreamReader sr3 = new StreamReader("file2.txt");
StreamReader sr2 = new StreamReader("file1.txt");
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader("file.txt");
strline = sr.ReadLine();
strarr = strline.Split(' ');
strline2 = sr2.ReadLine();
strarr2 = strline2.Split(' ');
strline3 = sr3.ReadLine();
strarr3 = strline3.Split(' ');
double x = double.Parse(strarr[0]);
double a = double.Parse(strarr[1]);
double b = double.Parse(strarr[2]);
double X = double.Parse(strarr[3]);
double Y = double.Parse(strarr[4]);
bool A = bool.Parse(strarr[5]);
bool B = bool.Parse(strarr[6]);
bool C = bool.Parse(strarr[7]);
string FirstName = strarr[8];
string Surname = strarr[9];
double x1 = double.Parse(strarr3[0]);
double y1 = double.Parse(strarr3[1]);
double Y1 = double.Parse(strarr2[2]);
int ans = int.Parse(strarr2[1]);
switch (ans)
{
case 1:
Console.WriteLine("\n The Given Co-Ordinate ({0},{1}) Lies Inside The Shaded Area", x1, y1);
break;
case 2:
Console.WriteLine("\n The Given Co-Ordinate ({0},{1}) Lies Outside The Shaded Area", x1, y1);
break;
}
Console.WriteLine("\n The Value Of Y Is {0}", Y1);
Console.WriteLine("\n ***** Initial Data*****:\n");
Console.WriteLine(" x={0} a={1} beta={2}", x, a, b);
Console.WriteLine(" x={0} Y={1} ", X, Y);
Console.WriteLine(" A={0} B={1} C={2}", A, B, C);
Console.WriteLine(" Nmae={0}", FirstName);
Console.WriteLine(" Surname={0}", Surname);
Console.WriteLine("\n ***** Results *****:\n");
Console.WriteLine(" Arithmetic equation: y = {0}", strarr2[2]);
Console.WriteLine(" Logical equation: Z = {0}", strarr2[0]);
strarr = strline.Split(' ');
fullname = strarr[8] + " " + strarr[9];
Console.WriteLine(" string type: fullname = {0}", fullname);
Console.WriteLine(" Number of letters in the full name = {0}", fullname.Length);
Console.WriteLine(" Number of letters in the name = {0}", strarr[8].Length);
Console.WriteLine(" Number of letters in the name = {0}", strarr[9].Length);
sr.Close();
sr2.Close();
sr3.Close();
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
input();
condition();
output();
}
}
}
---------------------------------------------------------------
6) Write a program MaxMin.cpp that reads in integers (as many as the user enters) and prints out the maximum and minimum values read in.
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication20
{
class Program
{
static void input()
{
string strline;
string[] strarr;
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader("file.txt");
strline = sr.ReadLine();
strarr = strline.Split('\t');
double x = double.Parse(strarr[0]);
double a = double.Parse(strarr[1]);
double b = double.Parse(strarr[2]);
double X = double.Parse(strarr[3]);
double Y = double.Parse(strarr[4]);
bool A = bool.Parse(strarr[5]);
bool B = bool.Parse(strarr[6]);
bool C = bool.Parse(strarr[7]);
string FirstName = strarr[8];
string Surname = strarr[9];
Console.WriteLine("\n ***** Initial data*****:\n");
Console.WriteLine(" x={0} a={1} beta={2}", x, a, b);
Console.WriteLine(" X={0} Y={1}", X, Y);
Console.WriteLine(" A={0} B={1} C={2}", A, B, C);
Console.WriteLine(" Name={0}", FirstName);
Console.WriteLine(" Surname={0}", Surname);
Console.ReadLine();
sr.Close();
}
static void condition()
{
string strline1;
string[] strarr1;
string[] a = new string[2];
double denom=0,num=0,y1=0;
bool Z1=true;
StreamReader sr1 = new StreamReader("file.txt");
strline1 = sr1.ReadLine();
strarr1 = strline1.Split('\t');
double x1 = double.Parse(strarr1[0]);
double a1 = double.Parse(strarr1[1]);
double X1 = double.Parse(strarr1[3]);
double Y1 = double.Parse(strarr1[4]);
bool A1 = bool.Parse(strarr1[5]);
bool B1 = bool.Parse(strarr1[6]);
bool C1 = bool.Parse(strarr1[7]);
num = Math.PI + Math.Atan(Math.Pow(x1, 2) + Math.Pow(a1, 5)) - Math.Pow(1 + (x1 * a1), 0.5) + Math.Asin(a1 - 0.5 * Math.Pow(10, -3));
denom = 4.8 * Math.Pow(10, 2.6) - Math.Log(Math.Abs(x1 - a1), 3) + 7 * Math.Exp(-x1) + Math.Pow(Math.Log(x1), 2) + Math.Atan(a1 * x1);
y1 = num / denom;
Z1 = A1 && C1 && Y1 >= 2.5 * Math.Pow(10, -5) || !(A1 || B1 && Y1 <= 1.3);
StreamWriter sr2 = new StreamWriter("file1.txt");
sr2.Write(y1 + "\t");
sr2.Write(Z1);
sr2.Close();
}
static void output()
{
string strline2,fullname;
string[] strarr2;
StreamReader s2 = new StreamReader("file1.txt");
strline2 = s2.ReadLine();
strarr2 = strline2.Split('\t');
Console.WriteLine("\n ***** Results *****:\n");
Console.WriteLine(" Arithmetic equation: y={0}", strarr2[0]);
Console.WriteLine(" Logical equation: Z={0}", strarr2[1]);
StreamReader s3 = new StreamReader("file.txt");
strline2 = s3.ReadLine();
strarr2 = strline2.Split('\t');
fullname = strarr2[8] + " " + strarr2[9];
Console.WriteLine(" String type: FullName={0}",fullname );
Console.WriteLine(" Number of letters in the full name={0}",fullname.Length );
Console.WriteLine(" Number of letters in the name ={0}", strarr2[8].Length);
Console.WriteLine(" Number of letters in the surname={0}", strarr2[9].Length);
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void Main()
{
input();
condition();
output();
}
}
}
-------------------------------------------
9) Write a program to convert currency from pounds sterling into deutsch marks. Read the quantity of money in pounds and pence, and output the resulting foreign currency in marks and pfennigs. (There are 100 pfennigs in a mark). Use a
const to represent the conversion rate, which is 2.31DM to £1 at the time of writing. using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace task_6_2_var_9
{
class Program
{
static void conversion(int pou, double pen)
{
double sterling;
double deutchmarks;
sterling = pou + (pen / 100);
deutchmarks = sterling * 231;
Console.Write("\n There Are {0} marks ", (int)deutchmarks / 100);
Console.Write("\n There Are {0} pfennings ", deutchmarks % 100);
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void Main (string[] args)
{
double pence;
int pounds;
Console.Write("\n Enter the pounds : ");
pounds = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("\n Enter the pence : ");
pence = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
conversion(pounds, pence);
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------9) An array E(m,n) is given. Write a program that changes places of elements in the i-th and k-th rows:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
int[,] E =new int [4,4] {{1,8,9,16},{2,7,10,15},{3,6,11,14},{4,5,12,13}};
for(int j=0 ; j<4 ; j++)
{
int temp;
temp = E [0,j];
E[0,j]=E[3,j];
E[3,j]=temp ;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
Console.Write("E[{0},{1}]={2} ", i, j, E[i, j]);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}
9) Write a program that asks a user to type n integers and prints out a number of positive numbers and all of the positive numbers in the same line in brackets.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication8
{
class Program
{
static void Main (string[] args)
{
int n, k ;
k = 0;
Console.WriteLine("Enter n");
n = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
int[] a = new int[n];
int[] b = new int[n];
Console.WriteLine("Enter numbers");
for(int i=0 ; i<n ; i++ )
a[i]= Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
for ( int j=0 ; j<n ; j++ )
if (a[j] > 0)
{
b[k] = a[j];
k++;
}
Console.WriteLine("Result");
Console.WriteLine("{0}",k);
Console.WriteLine("Array");
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
Console.Write(" {0} " , b[i]);
}
}
}
-----------------------------------------------------
Write a program that asks a user to type n integers and prints out a number of positive numbers and all of the positive numbers in the same line in brackets.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication8
{
class Program
{
static void Main (string[] args)
{
int n, k ;
k = 0;
Console.WriteLine("Enter n");
n = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
int[] a = new int[n];
int[] b = new int[n];
Console.WriteLine("Enter numbers");
for(int i=0 ; i<n ; i++ )
a[i]= Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
for ( int j=0 ; j<n ; j++ )
if (a[j] > 0)
{
b[k] = a[j];
k++;
}
Console.WriteLine("Result");
Console.WriteLine("{0}",k);
Console.WriteLine("Array");
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
Console.Write(" {0} " , b[i]);
}
}
}
-----------------------------------------------
c++
Write a program that asks a user to type in all the integers between 8 and 23 (both included) using a while loop.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
class WhileLoop
{
public static void Main()
{
int myInt = 8;
while (myInt <= 23)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", myInt);
myInt++;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
---------------------------------------------------
c++
) Write a program that asks a user to type in the value of N and computes N! with using for loop.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication17
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int k=1;
int n = Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
for(int i=1; i<=n ; i++)
{
k = k * i;
}
Console.WriteLine("Result={0}", k);
}
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
تاريخچه و سير تحول نقشه
در گذشته هاي دور ، از ترسيم به عنوان شكلي از هنر براي بيان احساسات و زيباييها و يا روشي براي ارسال و ابلاغ نظريات و ايده ها استفاده مي شد.
بشر اوليه عكس حيوانات را روي ديوار غارها ترسيم ميكرد كه اين خود مقدمهاي براي خلق و ايجاد نقشه به حساب مي آيد .
بعد از گذشت قرنها در 2000 سال قبل ا زميلاد مسيح بشر آموخت كه براي ترسيم و تفهيم افكار خود به جاي ديوار غارها و سنگها از پوست آهو استفاده كند.لئوناردو داوينچي هنرمند نقاشي مشهور ايتاليا باري عملي شدن طرحاي خود از تصاوير سه بعدي و نما به صورت كروكي و آزمايشي استفاده مي كرده است . شايد اولين نقشه هاي كشيده شده كه در دست است مربوط به مهندسين كلداني باشد كه بر روي يك تخته سنگ كشيده شده است وهم اكنون در موزه لوور پاريس از آن نگهداري مي شود. وسايلي كه معماران قديم استفاده مي كردند از از برنز ساخته مي شد و تقريبا شبيه وسايلي بود كه امروزه براي ترسيم نقشه ها استفاده مي كنند.
در قرن سيزده و چهارده ، نقشه ها به صورت تصاويري سه بعدي كشيده مي شدند .غالبا اين نقشه هاي سه بعدي ، يك تصوير ضميمه نيز به همراه داشتند كه تركيبي از نماي بالا با تصاويري از جلو يا از چپ بودند .
البته خواندن اين نقشه ها بسيار سخت و مشكل بود ، از اين رو با گذشت زمان دو تصوير تركيب شده از يكديگر جدا و حتي بعضي اوقات تصويري سومي را هم به آن اضافه مي كردند.
در اواخر قرن شانزدهم و اوايل قرن هفدهم كليه سفارشات و نياز هاي كارخانه ها به وسيله نقشه هايي تهيه مي شد كه تقريبا شبيه به نقشه هاي امروزي بود ، اما در اين نقشه ها از مقياس استفاده نمي شد ولي كليه قطعات ترسيم شده داراي ابعادو عدد اندازه بودند .
با پيشرفت فن كشتي سازي ، احتياج به نقشه هاي با دقت بيشتر احساس شد . نقشه هاي كه توسط ديا نوردان و يا همكاران آنها در قرن هجدهم كشيده مي شد ، داراي سه تصوير از جنسم مورد نظر بود.
در اين نقشه ها هر سه اندازه اصلي جسم يعني طول ، عرض ، و ارتفاع به خوب نشان داده مي شد.
در سال 1798 يك مهندس فرانسوي به نام گاسپارد مونژ كتابي در زمينه هندسه ترسيمس منتشر كرد ، كتابي كه اساس و بنيان رسم فني امروز را پايه ريزي كرد.
هندسه ترسيمي در قرن نوزدهم به سرعت توسعه و تكامل يافت تا اينكه امروزه كليه نقشه هايي كه در رشته هاي مختلف صنعتي ، رسم مي گرر پيرو اين قاعده بوده و معمولا داراي سه تصوير از يك جسم است.
به طور خلاصه مي توان گفت ، تهيه تصاويري از ساخته ها و مصنوعات به طريقي كه قابل درك براي ديگران باشد از نخستين ارزو هاي انسان در طول تاريخ بوده است ، لذا دسترسي به يك شيوه واحد به گونه اي كه امروز عمل مي شود با دشواريهاي فراوان و تحولات بسار همراه بوده است .
لكن امروزه با استعانت از شيوه هاي علمي ارائه شده به راحتي ميتوان با استفاده از روشهاي سنتي و يا رايانه ها ، قطعات پيچيده مكانيكي يا ساختمانها و تاسيسات بزرگ را به وسيله نقشه كشي به تصويري كشيده و براي ساخت در اختيار متخصصان قرار داد.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
C#
--------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
C#
IF STATEMENT
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication3
{
class Program
{
static void Main (string[] args)
{
double a, x, Y;
Console.WriteLine("\n Enter a value for x: ");
x = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("\n Enter a value for a: ");
a = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
if (x < 0)
Y = a * Math.Cos(Math.Pow(x, 2) / 2);
else
Y = a / 2 * Math.Exp(x / a) + Math.Exp(-x / a);
Console.WriteLine("\n The value of {0}", Y);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
--------------------------------------------
C#
if statement
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Ahmad
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double x, a, Y;
Console.WriteLine(" Enter a value for x : ");
x = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine(" Enter a value for a : ");
a = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
if (x < 0)
Y = 2 * a * Math.Pow(1 - Math.Pow(x/a ,2) , 1/2);
else
Y = a/2*Math.Cos(x)+3*a/2;
Console.Write(" The value of Y is {0}", Y);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}--------------------------------------
C#
IF STATEMENT
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication3
{
class Program
{
static void Main (string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Enter Coordinates \n");
double x, y;
x =
double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
y =
double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
if ((x <= 2) & (x >= -2) & (y >= -2) & (y <= 2) &
((x + y - 1 > 0) |
(-x + y + 1 < 0) |
(- x - y -1 > 0) |
(x - y + 1 < 0)))
Console.WriteLine("Point is inside");
else
Console.WriteLine("Point is outside");
}
}
}
---------------------------------------------------------------
C#
if statement
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Mehdi
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double x, a, Y;
Console.WriteLine(" Enter a value for x : ");
x = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine(" Enter a value for a : ");
a = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
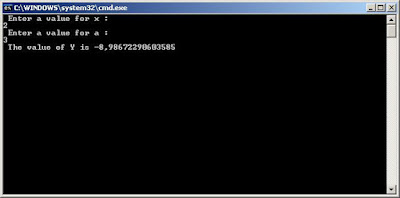
if (x <= (-6 * a))
Y = -Math.Pow(x + 3 * a, 2) - 2 * a;
else
Y = a * Math.Cos(x + 3 * a) - 3 * a;
Console.Write(" The value of Y is {0}", Y);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}-------------------------------------------------------
C#:
if statement
---------------------------------------------------------
C#:
using System;
namespace ex02{
/// <summary>
/// Summary description for Class1.
/// </summary>
class Class1
{
/// <summary>
/// The main entry point for the application.
/// </summary>
[STAThread]
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int intVar1 = 0;
int intVar2;
intVar2 = 1;
int intV3 = 15, intV4 = 12;
string strText1 = "abcd";
Console.WriteLine(
"The value for variables are : \n intVar1=" + intVar1 +
"\n intVar2=" + intVar2 +
"\n intV3=" + intV3 +
"\n intV4=" + intV4 +
"\n strText1=" + strText1);
Console.WriteLine("\n\n Press any key to terminate");
Console.ReadLine(); // pause screen!
}
}
}
----------------------------------------------------------------
C#:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace mehdi
{
class Program
{
static void Main ()
{
double
y,
alpha = 0.5 ,
x= 3.4 ,
beta= 1.65 ,
Denominator, Numerator,
X = 1.5,
Y = 2.5;
string FullName = "";
string FirstName = "mehdi";
string Surname = "moghadasi";
bool
Z,
A = true,
B = true,
C = false;
int
iFirstName ,
iSurname , iFullName;
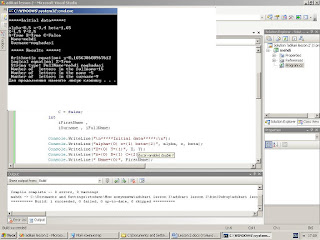
Console.WriteLine("\n*****Initial data*****:\n");
Console.WriteLine("alpha={0} x={1} beta={2}", alpha, x, beta);
Console.WriteLine("X={0} Y={1}", X, Y);
Console.WriteLine("A={0} B={1} C={2}", A, B,C);
Console.WriteLine(" Name={0}", FirstName);
Console.WriteLine(" Surname={0}", Surname);
Numerator =Math.Sin(Math.PI- beta/2) + Math.Log10(2*x + Math.Pow (alpha ,2 )) + Math.Pow(x,2) + Math.Pow(Math.Abs(x- Math.Pow(alpha , 3 )),1/4.0) ;
Denominator = Math.Exp(x + alpha) + Math.Pow(x, 3) + 5.4 * Math.Pow(10, -4) + Math.Tan(Math.Pow(x, 2) + 0.5 * Math.Pow(10, 2.1));
y = Numerator / Denominator ;
Z = A || B && X < Y || (X < 1.5 || B && C );
iFirstName = FirstName.Length;
iSurname = Surname.Length;
FullName = FirstName + " " + Surname;
iFullName = FullName.Length;
Console.WriteLine("\n ***** Results *****:\n");
Console.WriteLine(" Arithmetic equation: y={0}", y);
Console.WriteLine(" Logical equation: Z={0}", Z);
Console.WriteLine(" String type: FullName={0}", FullName);
Console.WriteLine(" Number of letters in the fullname={0}", iFullName);
Console.WriteLine(" Number of letters in the name ={0}", iFirstName);
Console.WriteLine(" Number of letters in the surname={0}", iSurname);
}
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------
C#:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double
y,
alpha = 0.5,
x = 3.4,
Denominator, Numerator,
X = 1.5, Y = 2.5;
double
beta = -3.35;
String FullName = "";
String FirstName = "Ahmad";
String Surname = "Jamialahmadi";
bool
Z,
A = true,
B = true,
C = false;
int
iFirstName,
iSurname, iFullName;
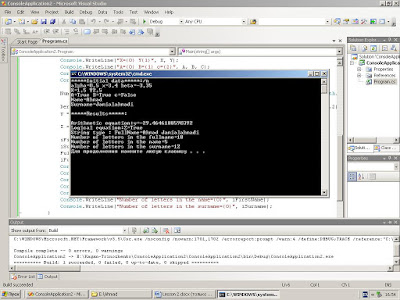
Console.WriteLine("*****Initial data*****:/n");
Console.WriteLine("alpha={0} x={1} beta={2}", alpha, x, beta);
Console.WriteLine("X={0} Y{1}", X, Y);
Console.WriteLine("A={0} B={1} c={2}", A, B, C);
Console.WriteLine("Name={0}", FirstName);
Console.WriteLine("Surname={0}", Surname);
Numerator = 1.9 * Math.Pow(10, 3) * x - Math.Exp(alpha * x) + Math.Asin(beta + x) - Math.Log10(Math.Pow(x, 2)) + alpha;
Denominator = Math.Pow(Math.Pow(alpha * x - 1.72 ,2), 1 / 3.0) + 4.75 * Math.Pow(10, 1.2) * (alpha - x) - Math.Pow(Math.Cos(beta - x), 2);
y = Numerator / Denominator;
Z = B || C && (X >= Y) || (X >= 5.5) && A || !B;
iFirstName = FirstName.Length;
iSurname = Surname.Length;
FullName = FirstName + " " + Surname;
iFullName = FullName.Length;
Console.WriteLine("\n*****Results*****:\n");
Console.WriteLine("Arithmetic equation:y={0}", y);
Console.WriteLine("Logical equation:Z={0}", Z);
Console.WriteLine("String type : FullName={0}", FullName);
Console.WriteLine("Number of letters in the fullname={0}", iFullName);
Console.WriteLine("Number of letters in the name={0}", iFirstName);
Console.WriteLine("Number of letters in the surname={0}", iSurname);
}
}
}

Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)